Why Are Bone Density Tests Important?
A bone density test provides you and your doctor with valuable information about the health of your bones. The bone density test reveals if you have normal bone density, low bone density (also called osteopenia), or osteoporosis.
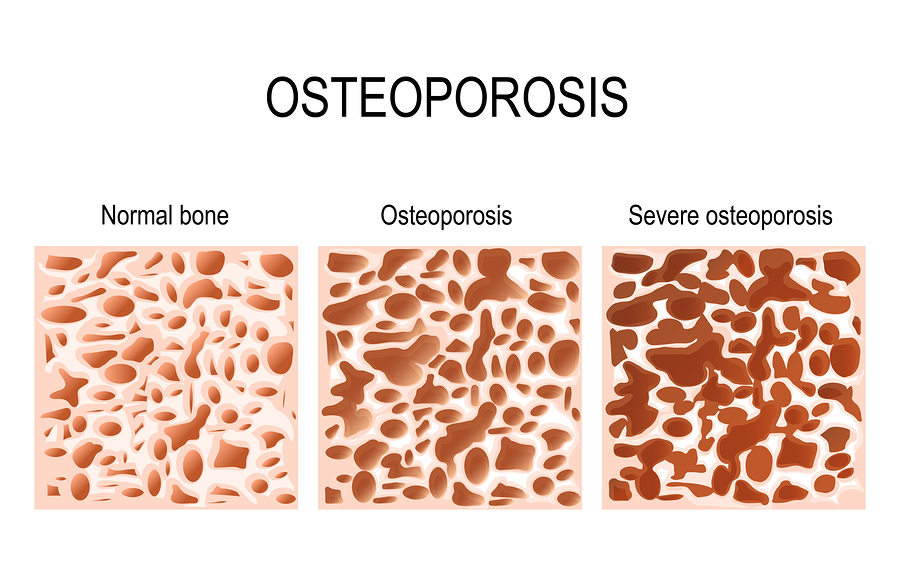
Osteoporosis is a condition in which a person has porous bones. As your bones become more porous and fragile, your risk of fracture or broken bones is greatly increased.
In addition, a bone density test is the only way your doctor can diagnose osteoporosis. This is important because if you have low bone density, you are at greater your risk of breaking a bone.
A bone density test, also called a bone mass measurement test, can help you and your healthcare provider:
- Determine if you have weak bones or osteoporosis before you break a bone
- Predict your chance of breaking a bone as you get older
- Provide information on your current bone density and whether it is improving, worsening, or staying the same
- Find out if your osteoporosis medicine is helping
- Diagnose osteoporosis after you have broken a bone
Who Should Have A Bone Density Test?
According to the National Osteoporosis Foundation (NOF), you should have a bone density test if you:
- Are a woman age 65 or older
- Are a man age 70 or older -- or a man age 50-69 with risk factors
- Break a bone after age 50
- Are a woman of menopausal age with risk factors
- Are a postmenopausal woman under age 65 with risk factors
The National Osteoporosis Foundation recommends having a bone density test if your x-ray results suggest a possible break or bone loss in the spine. Other reasons to have a bone density test include having back pain caused by a possible break in your spine, height loss of half an inch or more within one year, or total height loss of 1½ inches from your original height.
Types of Bone Density Tests
The most common bone density test is a central DXA test, which stands for dual energy x-ray absorptiometry. The National Osteoporosis Foundation recommends having a bone density test of your hip and spine using a central DXA machine to diagnose osteoporosis. DXA is the most common bone density test.
Peripheral testing machines check the finger, wrist, kneecap, shinbone, and heel. These machines are a good option when DXA scans are not available in certain communities. If bone density testing equipment is not available in your area, ask your doctor for recommendations on where to get the bone density test that is best for you.
Peripheral screening tests include:
- pDXA (peripheral dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry), which measures the wrist or heel.
- SXA (single-energy x-ray absorptiometry). This procedure measures the wrist or heel.
- QUS (quantitative ultrasound) uses sound waves to measure bone density.
Other peripheral screening tests include the pQCT (peripheral quantitative computed tomography), which measures the wrist, and RA (radiographic absorptiometry), which is a screening test that takes an x-ray of the hand.
Another screening tool called QCT (quantitative computed tomography) measures the spine, but measures other areas of the body, too. This test is done to determine how well osteoporosis treatment is working.
Call for a Free Consultation
Having a bone density test is important to your good health as you age. What’s more, taking care of sore joints is just as critical to living a healthy and active lifestyle. You don’t have to suffer with joint pain and discomfort.
Fortunately, Flexogenix® offers nonsurgical treatment options so you can avoid the risks associated with surgery and return to the activities you enjoy on a daily basis. Call us today at 1-888-YES-FLEX to schedule a free consultation to learn more about nonsurgical treatment options that help you enjoy an active life.